Research and Development
Itinerant Machinery
Itinerant machinery allows for the optimization and improvement of the valorization at the EVUP Network.

What is Itinerant Machinery?
 Itinerant machinery refers to a set of tools and equipment designed to be transported to different locations where they are needed. This system of organization and administration of the EVUP Network enables the stations to cooperate in optimizing resources and minimizing carbon emissions. This approach ensures that recycling machinery is fully utilized by stations.
The valorization process that takes place at the stations involves periods where treated material requires resting. This downtime is used to transform fixed machinery into itinerant recycling machinery. After a processing period, the material must undergo a resting phase, during which the machinery is not required at that particular station. As a result, the equipment can be moved to another station that needs processing.
Itinerant machinery refers to a set of tools and equipment designed to be transported to different locations where they are needed. This system of organization and administration of the EVUP Network enables the stations to cooperate in optimizing resources and minimizing carbon emissions. This approach ensures that recycling machinery is fully utilized by stations.
The valorization process that takes place at the stations involves periods where treated material requires resting. This downtime is used to transform fixed machinery into itinerant recycling machinery. After a processing period, the material must undergo a resting phase, during which the machinery is not required at that particular station. As a result, the equipment can be moved to another station that needs processing.
What are the Movements of Itinerancy?
The itinerancy process can vary based on the collected RPJ (Residues from Pruning and Gardening) in different communities and can also be influenced by climate conditions. The itinerant machines responsible for maintaining the material during the valorization process are specialized for different stages. Resting periods at a station can last up to a month and a half, and multiple batches of material may be at different stages of the process simultaneously, requiring careful coordination.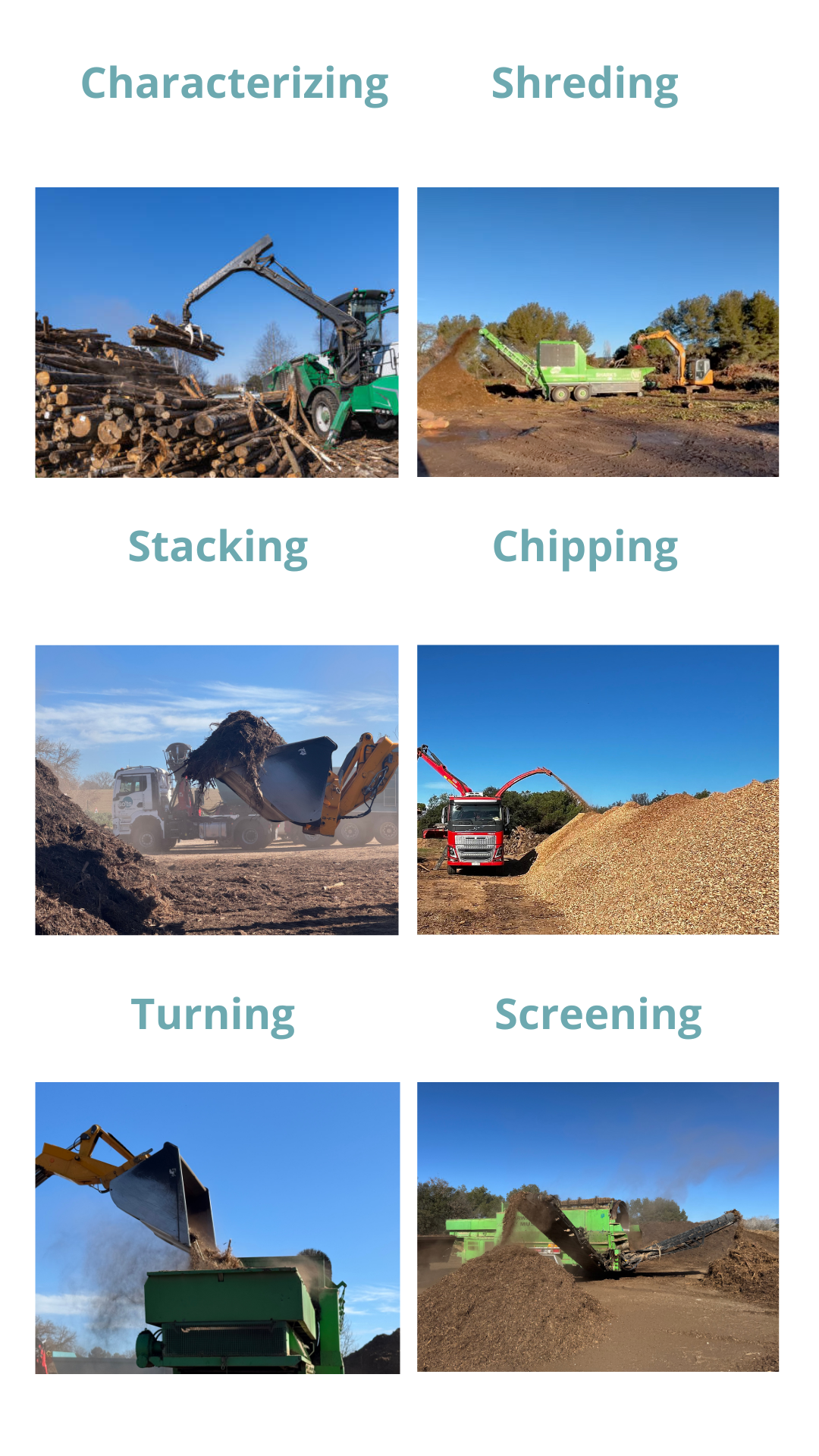 Following the processes mentioned in Operations, this machinery is used for the valorization of pruning and gardening waste deposited at the EVUP.
Following the processes mentioned in Operations, this machinery is used for the valorization of pruning and gardening waste deposited at the EVUP.
The Environmental and Economic Impact of the Itinerant Machinery System
Objective: Evaluate the environmental and economic impact of using itinerant machinery compared to a fixed machinery system.
 Methodology:
Methodology:
- Conduct a life cycle analysis (LCA) to compare carbon emissions and other environmental impacts of both systems.
- Collect data on operating, maintenance, and transport costs associated with itinerant and fixed machinery.
- Conduct interviews with operators and managers of Self-Managed EVUPs to gather qualitative feedback on the effectiveness and challenges of each system.
- Develop recommendations for the continuous improvement of the itinerant machinery system based on the results obtained.
Expected Impact: Identification of best practices to minimize environmental impact and maximize the economic efficiency of the EVUP Network, contributing to a more sustainable management of plant waste.
Optimization of Itinerant Machinery in the Valorization of Pruning and Gardening Waste (RPJ)
Objective: Analyze and optimize the movements and use of itinerant machinery across the different stations of the EVUP Network to maximize the efficiency of the plant waste valorization process.
Methodology:
- Collect data on the resting and processing periods of each type of waste at various stations.
- Develop logistical models to optimize machinery movements.
- Implement the proposed solutions and evaluate their effectiveness through field tests.
- Compare costs and operational efficiency before and after the implementation of improvements.
 Expected Impact: Improved coordination and use of machinery, reduced operational and transport costs, and increased efficiency in the valorization of plant waste.
Expected Impact: Improved coordination and use of machinery, reduced operational and transport costs, and increased efficiency in the valorization of plant waste.









