What is the valorization of vegetable waste?
The valorization of vegetable waste is a process of operations aimed at reintegrating materials considered waste back into the market after treatment. This approach seeks to return value to these materials, transforming them into useful resources through various techniques such as composting, shredding, or biogasification. Essentially, it involves converting
discarded vegetable waste into value-added products, contributing to more sustainable and efficient management of natural resources.
What is the purpose of valorization?
The primary purpose of the valorization of vegetable waste is to reduce the environmental impact it can generate. Poor management of vegetable waste can cause harmful effects on the planet, such as soil and water pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Valorization aims to reverse these negative impacts by transforming waste into positive outcomes. Additionally, this process conserves natural resources and promotes the circular economy.

What is processed at a Sots Station?
The valorized materials at a Sots Station consist of a specific selection of waste classified as 20 02 01, known as RPJ, which includes:
- Clean pruning and gardening waste
- Tree and shrub stumps
- Shredded pruning waste
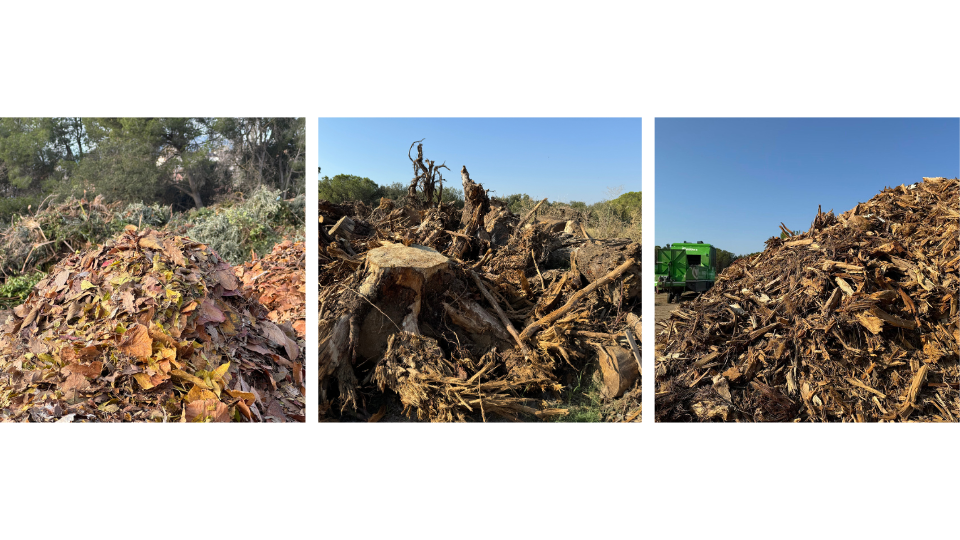

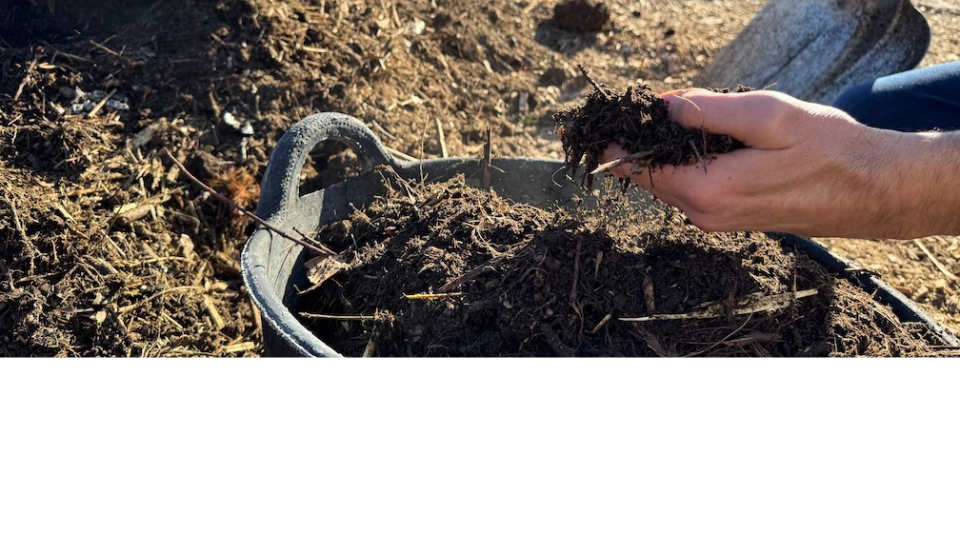
Products, by-products, and production waste from a Sots Station
Each process at a Sots Station results in gains and consequences in the form of products, by-products, and waste. The station provides opportunities for research and development of new processes for creating innovative products, advancing both technology and biology.
What research is intended to be conducted?
The research currently being initiated at Sots Stations, particularly in the fields of biology and forestry science, aims to find new applications and products from materials that are presently considered waste. To achieve this, Sots Verds has partnered with the
CTFC, the Center for Forest Science and Technology of Catalonia, which is collaborating to maximize the yield from all the processes and materials gathered at Sots Stations.
The main research areas are summarized in these four topics:
The valorization of semi-processed screened wood chips
Objectives:
- Determine potential applications of semi-processed screened wood chips in various industrial sectors.
- Assess the effectiveness of screening in separating usable materials from waste.
- Establish a model for the economic valorization of semi-processed screened wood chips.
- Reduce environmental impact by reusing semi-processed screened wood chips.
Research Questions:
- What are the physical and chemical characteristics of semi-processed screened wood chips?
- Which sectors can use semi-processed screened wood chips as raw material?
- What are the costs and benefits associated with the valorization of semi-processed screened wood chips?
- How can the screening process be improved to increase the amount of reusable material?

The applications of the 0-10, 0-20 / +30 / G30 screening waste
Objectives:
- Identify potential applications for different fractions of screening waste.
- Develop strategies for the valorization of 0-10, 0-20 / +30, and G30 screening waste.
- Reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills through reuse and recycling.
Research Questions:
- What are the physical and chemical properties of the different fractions of screening waste?
- How can screening waste be applied in construction, agriculture, or other sectors?
- What are the economic and environmental impacts of valorizing screening waste?
- What technologies can be implemented to improve the separation and valorization of screening waste?
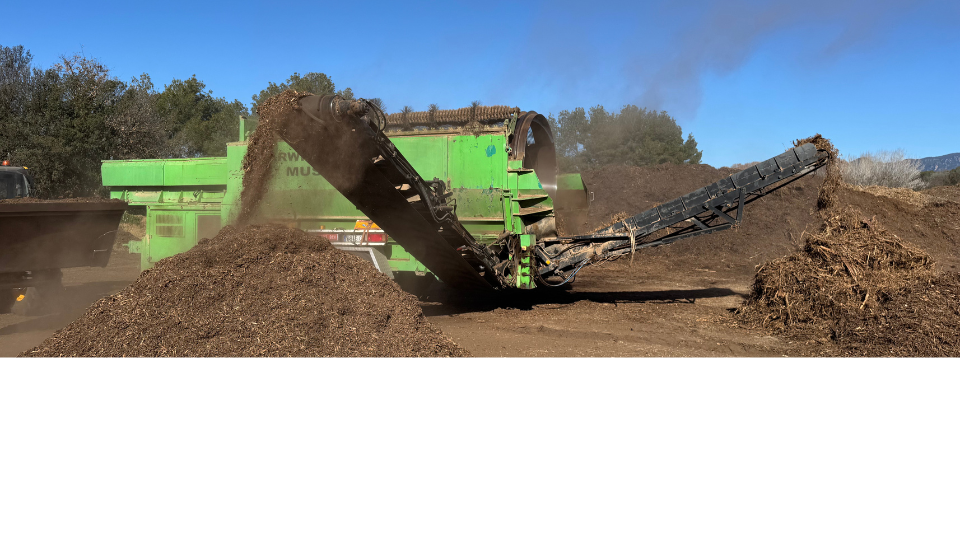

The Valorization of Biomass Production / Bedding / Dry and Wet Mulching
Objectives:
- Increase the efficient use of biomass, bedding, and mulching for agricultural and energy applications.
- Reduce agricultural waste by converting it into useful biomass.
- Analyze the economic and environmental benefits of using dry and wet mulching.
Research Questions:
- What are the nutritional and energy properties of biomass, bedding, and mulching?
- How can biomass production processes be optimized to maximize its valorization?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of dry and wet mulching in different types of crops?
- What impact does the valorization of biomass, bedding, and mulching have on agricultural sustainability and waste reductio
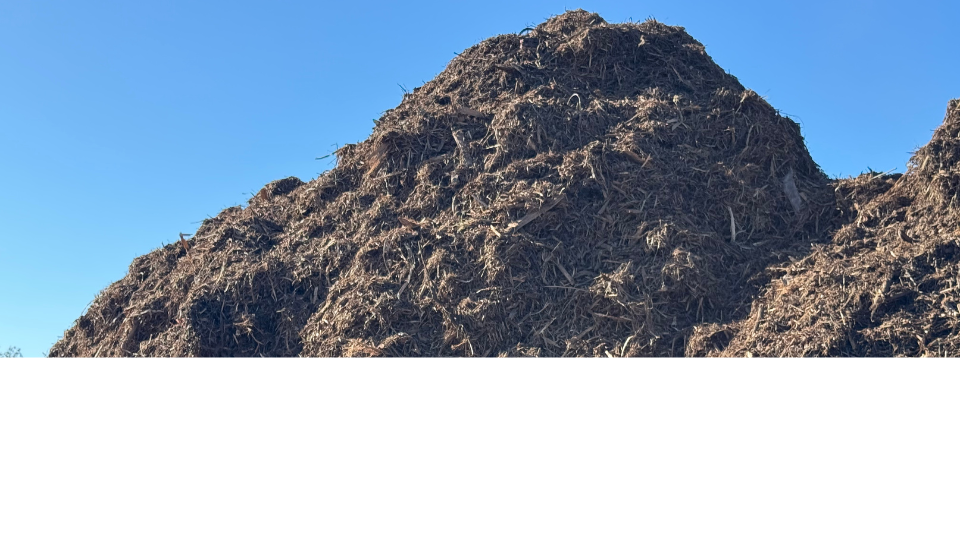


 The valorization of vegetable waste is a process of operations aimed at reintegrating materials considered waste back into the market after treatment. This approach seeks to return value to these materials, transforming them into useful resources through various techniques such as composting, shredding, or biogasification. Essentially, it involves converting discarded vegetable waste into value-added products, contributing to more sustainable and efficient management of natural resources.
The valorization of vegetable waste is a process of operations aimed at reintegrating materials considered waste back into the market after treatment. This approach seeks to return value to these materials, transforming them into useful resources through various techniques such as composting, shredding, or biogasification. Essentially, it involves converting discarded vegetable waste into value-added products, contributing to more sustainable and efficient management of natural resources.














