Awareness
Understanding the context to comprehend the process
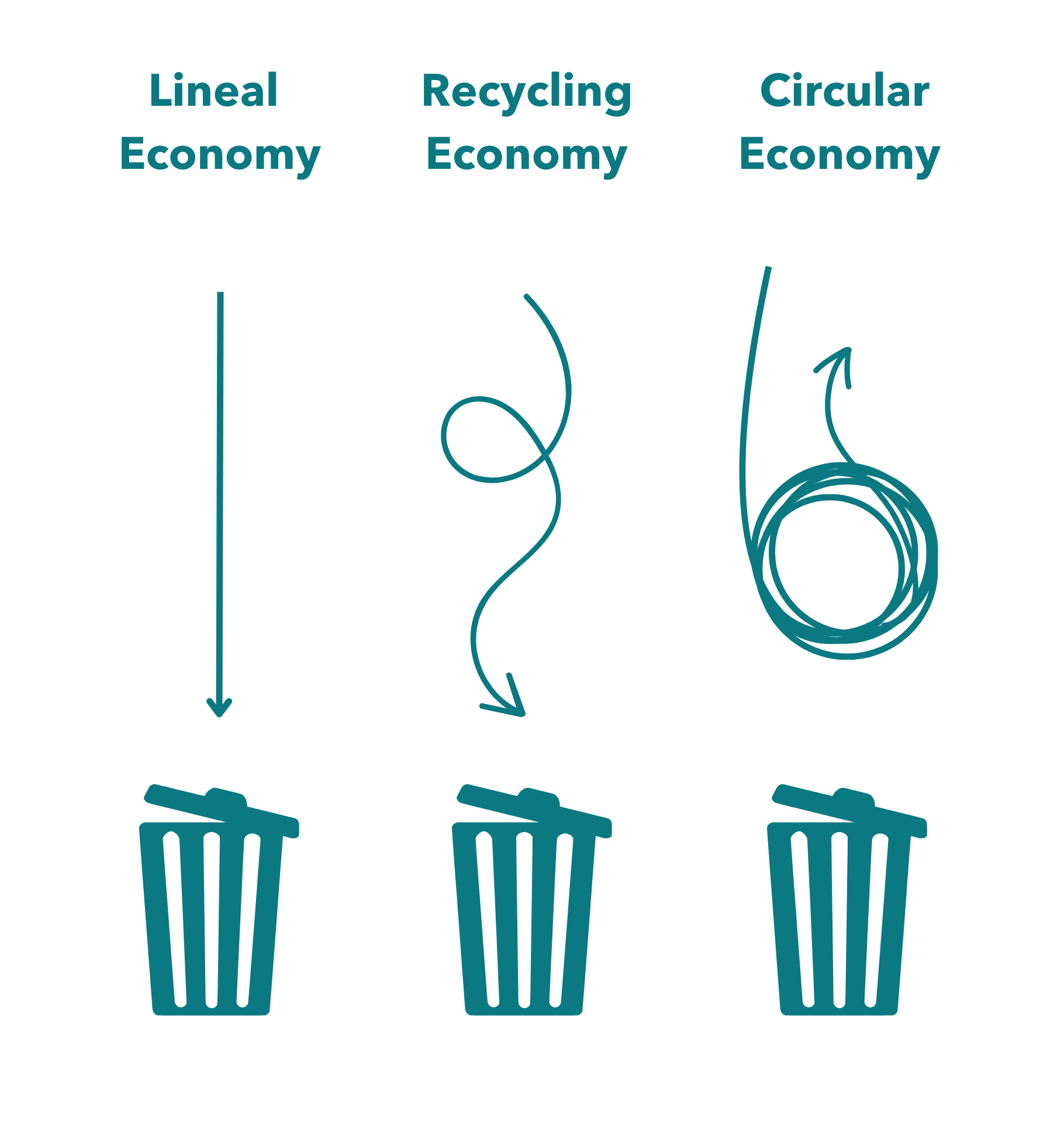
What is the circular economy?
The circular economy is an economic model that focuses on waste reduction and resource reuse. Unlike the traditional linear economy model, which is based on the production, consumption, and discarding of products, the circular economy seeks to extend the lifespan of materials and products by keeping them in use for as long as possible. This is achieved through recycling, reuse, repair, and the valorization of waste.
A “second-life product” is the result of the circular economy. This term refers to products that, after their initial useful life, are reintroduced into the economic cycle once the necessary valorization and transformation processes have been completed. The circular economy promotes more efficient and sustainable resource management, reducing environmental impact and encouraging innovation and social responsibility.
What is bioeconomy?
Bioeconomy is an economic model that focuses on the sustainable use of renewable biological resources for the production of goods, services, and energy. This approach integrates agricultural, forestry, fishery, and industrial activities, as well as biotechnology, to develop innovative products that replace fossil and non-renewable materials. Bioeconomy promotes the conservation and efficient use of natural resources, driving environmental sustainability, waste reduction, and greenhouse gas emissions. At the same time, it fosters economic and technological competitiveness by creating green jobs, contributing to the development of a more balanced and environmentally respectful economy.

What does research and development mean?
Research and development (R&D) refers to innovative processes carried out to discover new strategies and concepts. When applied, these allow for the development of new products, services, or processes, or the improvement of existing ones. Research involves scientific and technical investigation to acquire new knowledge, while development applies that knowledge to create innovations that can be marketed or used to enhance efficiency and competitiveness. R&D is fundamental to technological and economic progress, driving all sectors forward.

What is material dependency?
Material dependency refers to the need for a country, company, or economy to obtain materials, natural resources, or products from other regions or countries. It signifies the reliance on external sources for essential goods. This dependency can lead to economic, political, and environmental vulnerabilities, particularly in the face of price fluctuations, supply disruptions, or geopolitical conflicts. Reducing this dependency involves diversifying resource sources, promoting recycling, innovating in alternative materials, and encouraging the circular economy to ensure more sustainable and secure resource management.

What is consumption?
Consumption is the act of buying and using goods and services to satisfy human needs and desires. It includes everything that individuals, families, businesses, and governments acquire and use daily, such as food, clothing, housing, energy, transportation, education, and entertainment. Consumption is a fundamental part of the economy, driving demand for products and services, influencing production, economic growth, and employment. However, excessive or unsustainable consumption can have negative impacts on the environment and natural resources, leading to an increasing focus on responsible and sustainable consumption.

What is responsible and sustainable consumption?
Responsible and sustainable consumption is the practice of buying and using goods and services in a way that minimizes negative impacts on the environment, society, and the economy while meeting personal needs. This approach involves making conscious decisions about what, how, and when to consume, considering factors like product durability, origin, production conditions, and the environmental and social effects of their manufacturing and use.
Key aspects include:
Reduce:
Minimizing unnecessary consumption and avoiding waste.
Reuse:
Opting for durable products and giving a second life to items.
Recycle:
Proper separation and recycling of materials to reduce waste.
Buy local:
Prioritizing local products to decrease transport emissions and support the local economy.
Choose eco-friendly and ethical products:
Preferring sustainably produced and ethically sourced goods.
Energy efficient:
Selecting products and services that consume less energy and natural resources.
This type of consumption promotes a fairer, more balanced economy that respects the planet, ensuring that future generations can also meet their needs.
What is local production and consumption?
Local production refers to the manufacturing and processing of goods and services within a specific geographical area, such as a city, region, or country, with consumption of these products by the local community. This model focuses on using locally available resources, labor, and raw materials, fostering a more resilient and sustainable economy.
En resumen, la producción local está en sinergia con el consumo local, contribuyendo a una economía más autosuficiente, sostenible y socialmente justa, beneficiando tanto al medio ambiente como a las personas que viven en la comunidad.
What is synergy?
Synergy refers to the interaction or cooperation of elements or parts of a system to achieve a result that is greater than the sum of the individual parts. It is the phenomenon where the combination of various elements produces an effect greater than the sum of the individual effects of those elements.
What is a product green passport?
A product green passport, or environmental label, certifies that a product has been manufactured, transported, or distributed in a way that minimizes environmental impact throughout its life cycle. This label provides consumers with clear and transparent information about the sustainability of the product, enabling informed choices that favor environmentally friendly products.
What is a valorized product?
A valorized product refers to an item that was previously considered waste but, after a treatment and handling process, has been transformed into a valuable resource or product that can be reintroduced into the market.
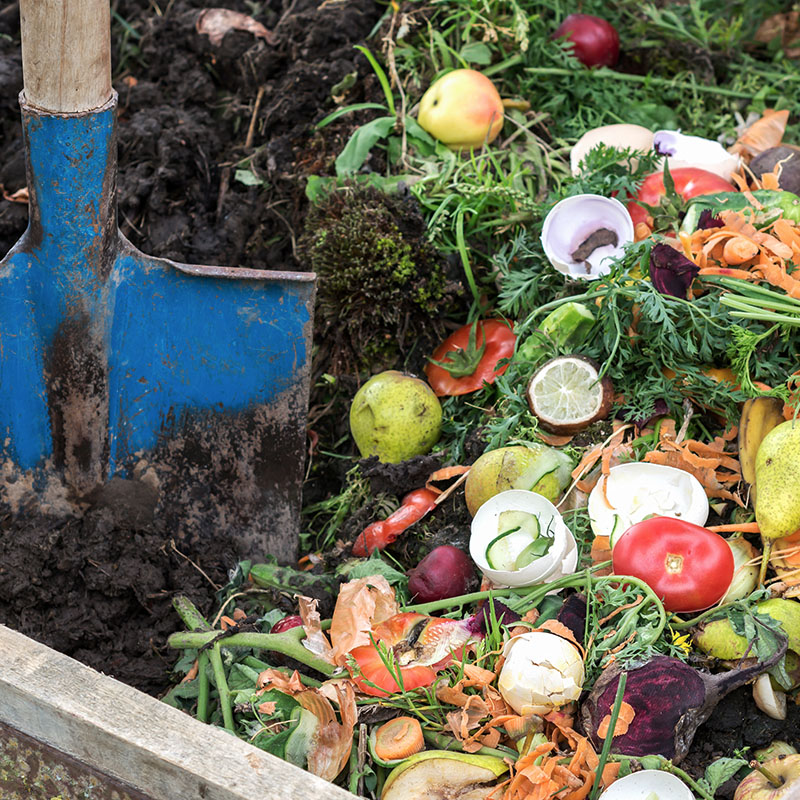

What is compost?
Compost is an organic product resulting from the controlled biological decomposition of organic materials such as food scraps, plant waste, paper, and cardboard. This decomposition process, known as composting, produces a nutrient-rich product used as a soil enhancer in gardening, agriculture, and horticulture. Compost improves soil fertility, enhances water retention, and supports sustainable agricultural practices by reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.

What is a by-product?
By-products are materials obtained as a result of a production process that can be managed as commercial products or substitute raw materials without the need for additional treatment operations. To qualify as by-products, these materials must have an assured subsequent use, be produced as part of a production process, and meet all relevant safety and environmental protection requirements.
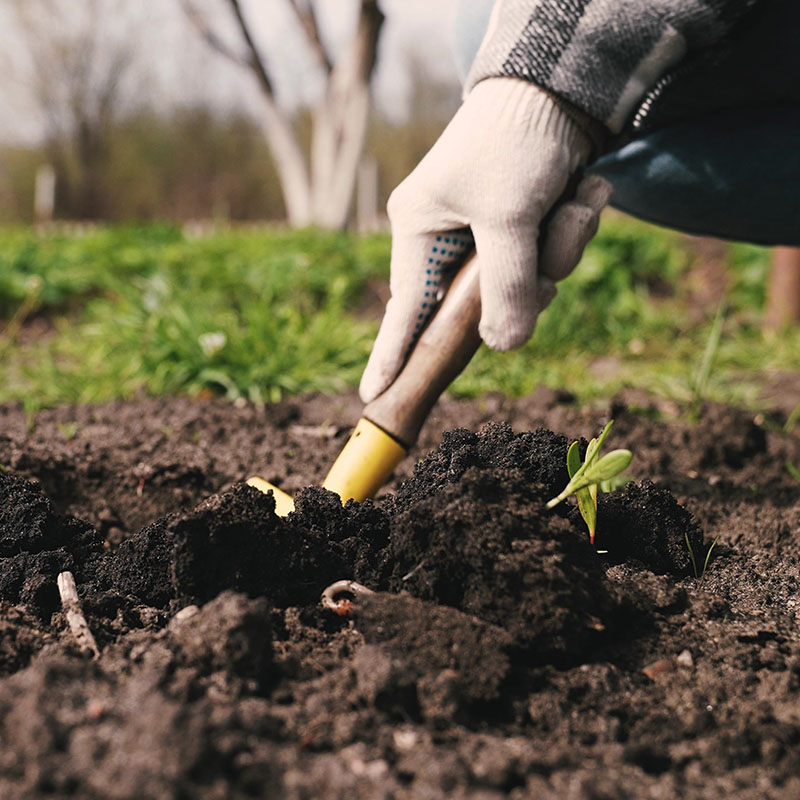

What is a substrate?
A substrate is a material used to support plant growth, providing a base for roots to anchor and obtain nutrients. Substrates vary in composition and properties depending on their intended use and the specific needs of the plants. Common substrates include mixtures of soil, perlite, vermiculite, and coconut fiber.
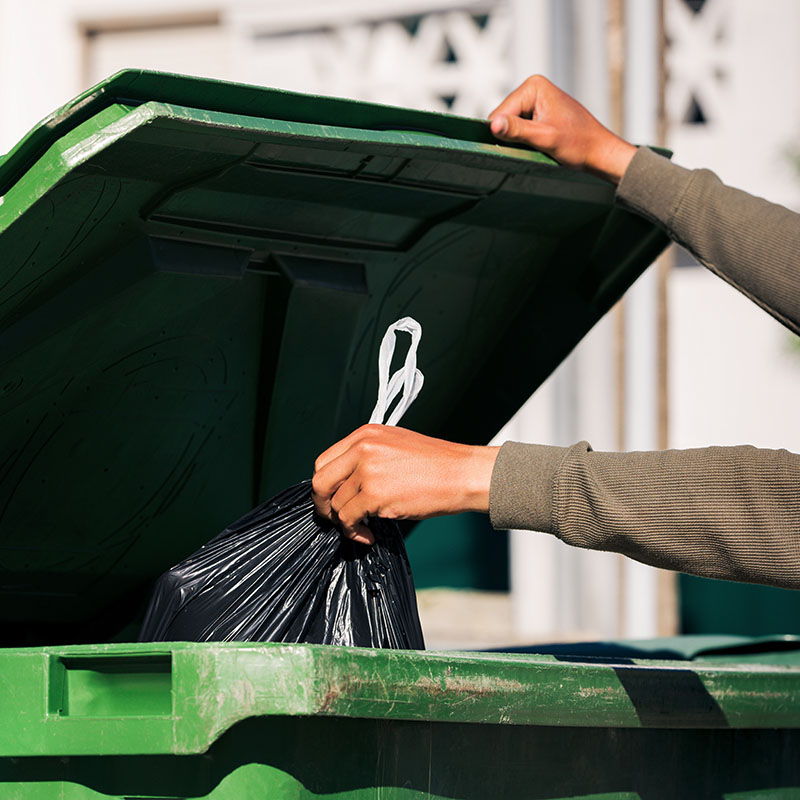

What is waste?
Waste is any material or substance considered unnecessary, undesirable, or discarded after a specific process or use. Waste can be solid, liquid, or gaseous, and proper waste management is essential for minimizing its negative impact on human health and the environment. This includes practices such as source reduction, recycling, reuse, valorization, and proper disposal.
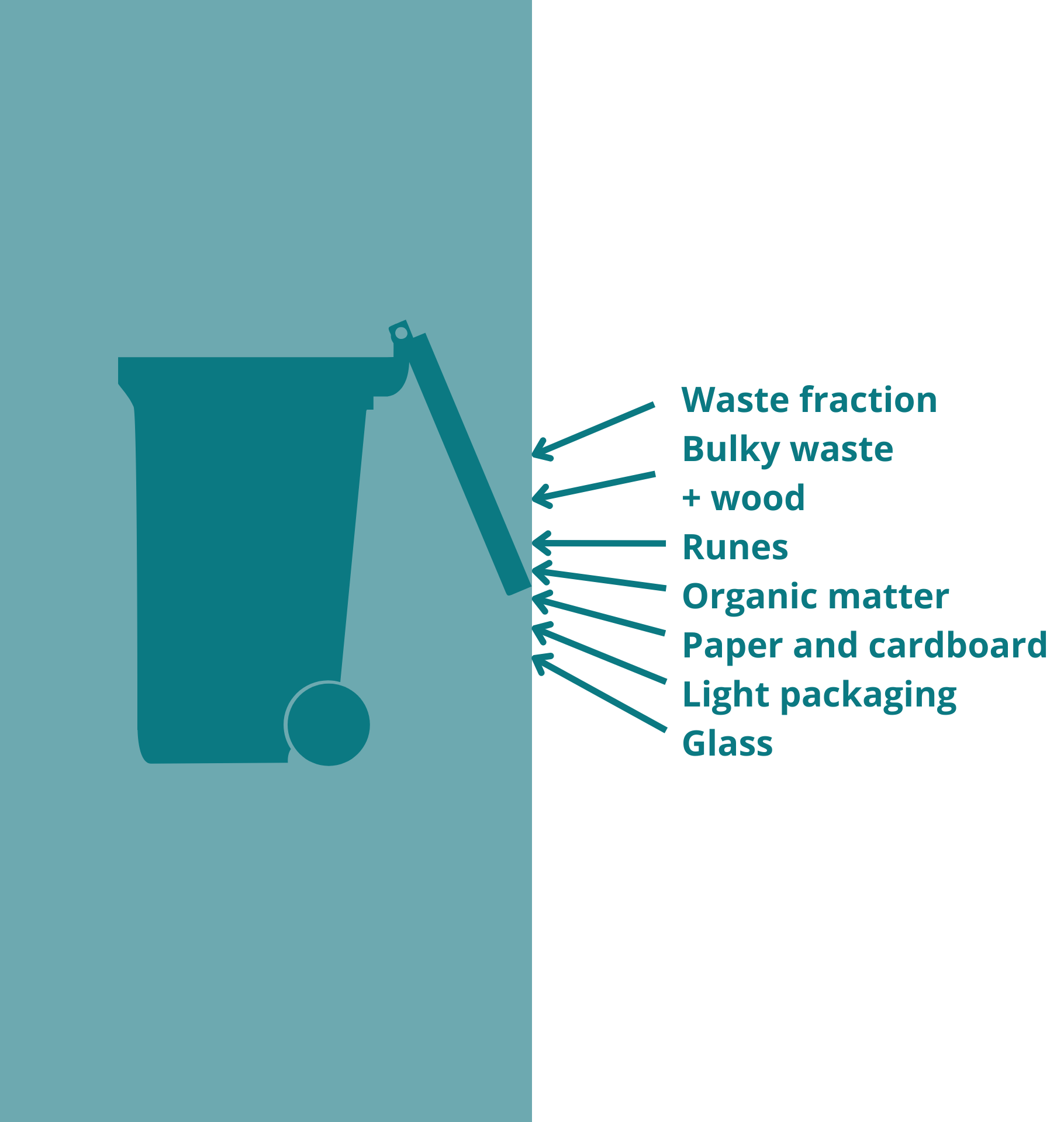
What is urban waste?
Urban waste, also known as municipal waste, is waste generated in urban areas as a result of daily activities of residents, businesses, and institutions. This type of waste includes a variety of discarded materials from homes, shops, offices, and urban facilities.
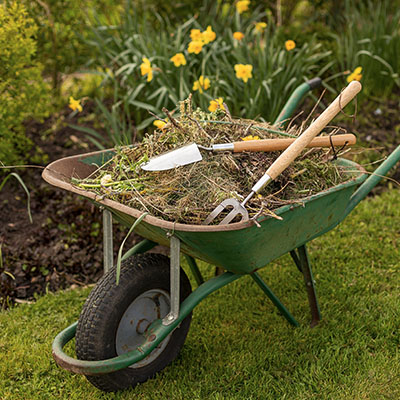

What do the initials FV stand for?
FV stands for “Fração Vegetal” (Plant Fraction), referring to biodegradable organic material of plant origin that is susceptible to biological degradation. It can be divided into small non-woody plant waste (like grass and leaves) and larger woody waste (like prunings), which require shredding for valorization.
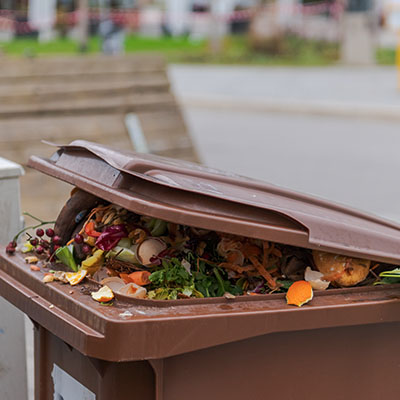

What do the initials FORM stand for?
FORM stands for “Fracción Orgánica de los Residuos Municipales” (Organic Fraction of Municipal Waste), referring to biodegradable organic waste of plant or animal origin, including food scraps and small plant trimmings.
What is the difference between plant waste and organic waste?
The main difference is that plant waste specifically refers to material from plants, while organic waste includes all biodegradable materials, both plant and animal. Plant waste is a subset of organic waste.
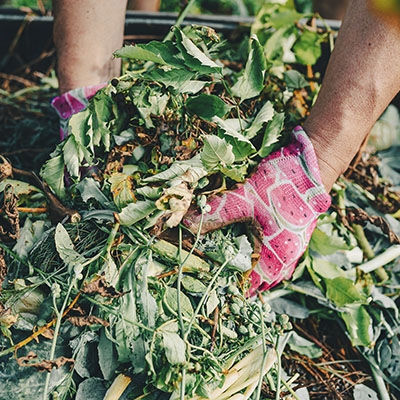

Vegetal Waste
Vegetal waste refers to all material of plant origin that is discarded after activities such as pruning, garden cleaning, tree felling, and other plant-related activities. This type of waste can include branches, leaves, grass clippings, flower stems, and other parts of plants.
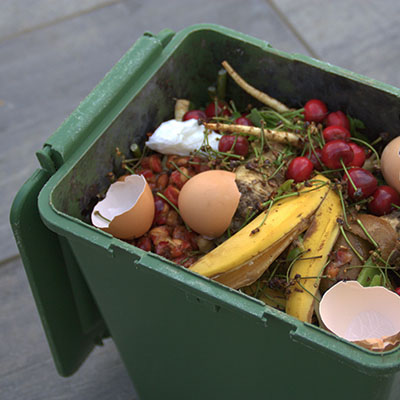

Organic Waste
This is a broader term that includes all biodegradable materials of organic origin, both plant and animal-based. It encompasses not only the previously mentioned vegetal waste but also food waste (such as food scraps, fruit peels, kitchen leftovers, etc.) and other organic materials that can be biologically decomposed.
In summary, all vegetal waste is organic because it comes from plant materials, but not all organic waste is specifically vegetal; it also includes materials of animal origin. The distinction between these two types of waste is relevant in waste management and in selective collection and valorization processes.
What is waste 20 02 01?
Waste 20 02 01 refers to biodegradable waste generated from municipal parks and gardens, such as grass, wood, leaves, and tree stumps. It falls under the European Waste List and is classified as plant residue, requiring proper valorization.
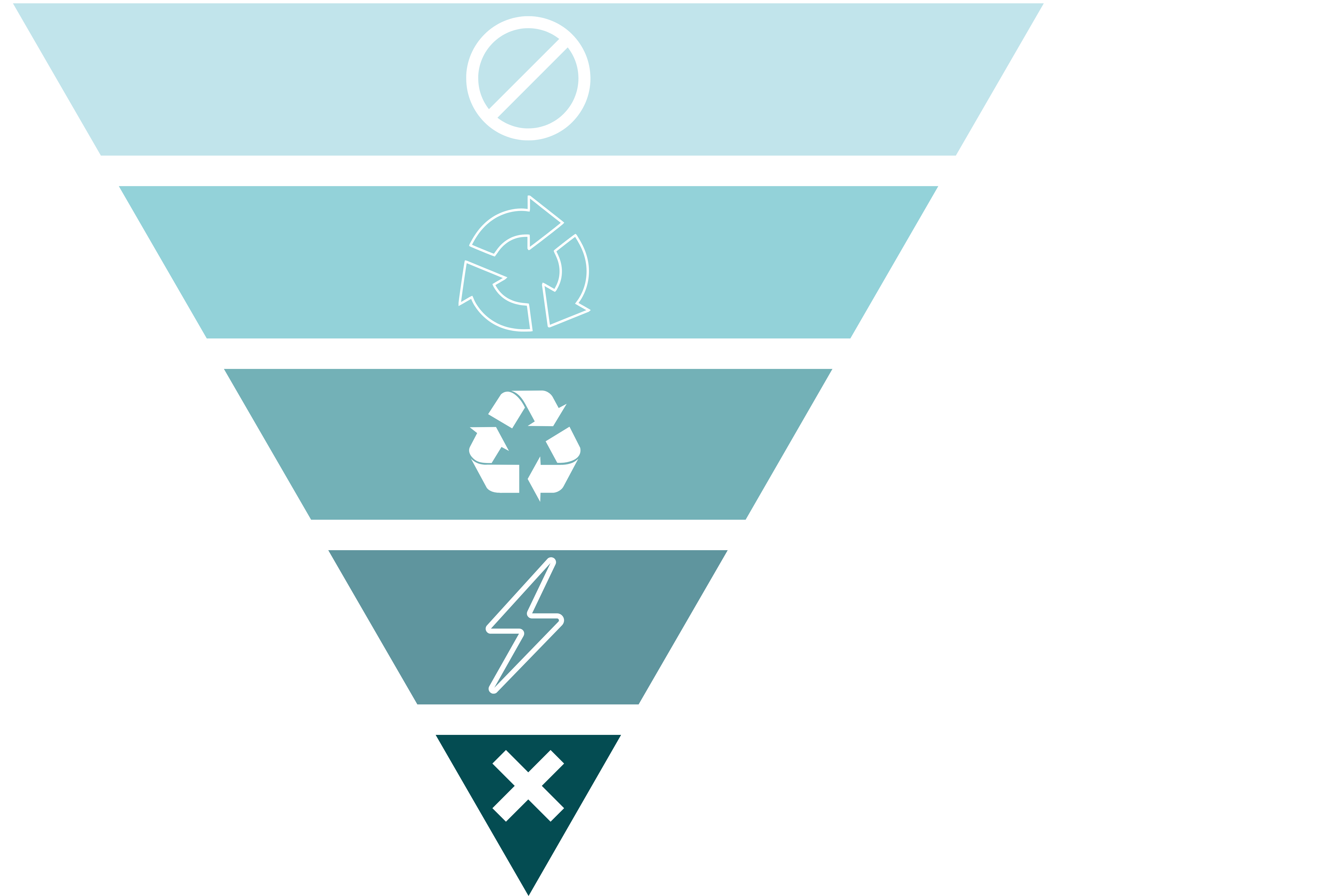
What is the waste hierarchy?
The waste hierarchy is a waste management principle that prioritizes reducing waste generation, followed by reuse, recycling, energy recovery, and finally disposal. It promotes sustainable practices and encourages valorization of waste materials to minimize environmental impact.